craftsman chainsaw 917.353710 30177 manual

Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 Manual Overview
This essential guide outlines safety rules, operating instructions, and maintenance procedures. It includes engine specifications, such as magneto air gap and breaker-point gap. Following this ensures safe, efficient operation and product support.

Understanding Manual Importance
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 manual is an indispensable resource for every owner. Its importance stems from providing comprehensive guidance, ensuring both user safety and optimal tool performance. Unlike mere digital files or low-quality photocopies, a well-produced manual offers clear, readable instructions, critical for proper understanding and application. It explicitly states that reading and following all Safety Rules and operating instructions is paramount before using the product. This vital document details how the low emission engine operates, differing significantly from older models, emphasizing the necessity of understanding these unique characteristics to prevent issues. Furthermore, the manual includes crucial information regarding regular maintenance schedules and troubleshooting steps, helping users identify and resolve common problems efficiently. It acts as a primary reference for accessing CRAFTSMAN parts and service, alongside detailing warranty specifics. Essentially, the manual safeguards the user, prolongs the chainsaw’s lifespan, and maintains its functional integrity, making it far more than just paper; it’s an essential accessory for unleashing the tool’s full potential and ensuring a reliable, safe user experience. Adherence to its contents is fundamental for responsible ownership and sustained operational excellence.

Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 Key Features
The Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 features a robust gas-powered engine. It boasts a low emission design, operating uniquely from previous models. This tool is suitable for diverse tasks like landscaping and efficient firewood cutting.
Robust Gas-Powered Engine
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 is equipped with a robust gas-powered engine, meticulously engineered to deliver consistent power and reliable performance for demanding cutting tasks. This engine’s inherent strength makes it an ideal choice for users tackling challenging outdoor projects, ensuring the chainsaw operates effectively even under strenuous conditions. Its gas-powered nature provides the freedom of movement unconstrained by power cords, allowing operators to navigate large properties or remote areas with ease. The engine’s design emphasizes durability, promising a long operational life when properly maintained according to the manual’s guidelines. This core feature enables the chainsaw to effortlessly cut through dense wood, making quick work of tough jobs. The power generated by this robust engine is precisely what allows the 917.353710 30177 to excel in a variety of applications, from intricate landscaping tasks requiring sustained power to the heavy-duty demands of cutting substantial amounts of firewood. Users can depend on this engine’s capability to maintain high performance levels, ensuring efficiency and productivity across all uses. Its engineering focuses on providing the necessary torque and RPMs for clean, effective cuts, solidifying its reputation as a truly dependable tool.
Low Emission Engine Characteristics
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 incorporates a state-of-the-art low emission engine, a significant advancement from previous generations. This design prioritizes reducing environmental impact by minimizing harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere during operation. Users will benefit from a cleaner working environment and a more eco-conscious tool. Crucially, this low emission technology means the engine operates differently from older, conventional engines. This distinction may involve unique starting procedures, specific fuel-air mixtures, or different warm-up routines to ensure emission control systems function optimally. Familiarity with these operational nuances, as detailed in the user manual, is paramount for unlocking the engine’s full potential and maintaining its low emission profile. The innovative engineering behind this engine not only meets current environmental regulations but also anticipates future standards, providing a forward-thinking solution for outdoor power equipment. Its distinct operational characteristics contribute to improved fuel efficiency and smoother power delivery, enhancing the overall user experience while significantly lessening its ecological footprint. This commitment to cleaner operation underscores the chainsaw’s modern design philosophy, ensuring powerful performance alongside environmental stewardship.
Differing Engine Operation

The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 features a low emission engine, which necessitates a distinct operational approach compared to older chainsaw models. This engine operates differently from previous designs, requiring users to adapt. For instance, start-up procedures might be more precise, requiring specific choke settings or priming sequences to ensure optimal fuel delivery and combustion for reduced emissions. The engine’s idle characteristics could also vary, potentially running at a slightly different RPM or exhibiting a smoother, quieter hum due to advanced internal components designed for efficiency and cleanliness. Furthermore, the throttle response might feel more refined, reflecting the engine’s optimized performance curve tailored for lower environmental impact. It is crucial for operators to thoroughly review the manual, as understanding these specific operational nuances is key to maximizing the chainsaw’s performance, ensuring its longevity, and maintaining its low emission compliance. Ignoring these differences could lead to suboptimal performance or even premature wear. This advanced engineering ensures powerful cutting while adhering to modern environmental standards. Strict adherence to the manual’s guidelines for starting, running, and shutting down the engine will guarantee the best user experience.

Versatile Task Suitability
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 is engineered with a robust gas-powered engine, making it exceptionally suitable for a wide array of demanding tasks. Its inherent power and reliable performance allow users to confidently approach diverse cutting challenges, from routine yard work to more intensive projects. This versatility stems from its well-balanced design, which combines sufficient horsepower with ease of handling, ensuring efficient operation across various applications. Users will find it an indispensable tool for maintaining their property, tackling unexpected outdoor situations, and preparing materials. The chainsaw’s capability extends beyond basic cutting, proving effective in scenarios requiring sustained effort and precision. It’s not just about raw power; it’s about the consistent delivery of that power in different contexts, allowing for adaptability. Whether the job calls for limbing fallen branches, clearing dense undergrowth, or even assisting in more intricate woodcraft where controlled cuts are paramount, this model rises to the occasion. Its design prioritizes operational flexibility, ensuring that homeowners and seasoned professionals can leverage its capabilities for successful task completion, making it a truly multi-functional piece of equipment ready for almost anything thrown its way.
Landscaping Use Cases
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 proves exceptionally effective for a diverse range of landscaping applications, thanks to its robust gas-powered engine. Owners will find it an invaluable tool for maintaining the aesthetic and health of their outdoor spaces. For instance, it excels at precise branch trimming, allowing for the shaping of ornamental trees and shrubs, which greatly enhances property curb appeal. Its power makes quick work of overgrown brush and dense foliage, facilitating garden clean-ups and preparing areas for new plantings. Furthermore, the chainsaw is ideal for efficiently clearing fallen limbs after storms, ensuring safe access and preventing further damage to surrounding vegetation. Its capability to handle various wood types and sizes means it can manage everything from light pruning tasks to more substantial clearing operations. This versatility greatly streamlines yard maintenance, reducing manual effort and time spent. Whether it’s for routine upkeep, significant landscape overhauls, or simply keeping pathways clear, the 917.353710 30177 model delivers consistent, reliable performance. It enables users to achieve professional-looking results in their own backyards, making demanding landscaping chores both manageable and highly efficient.
Firewood Cutting Capabilities
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 is exceptionally well-suited for firewood cutting, a critical task for many homeowners and outdoor enthusiasts. Its robust gas-powered engine provides the necessary power and torque to efficiently process logs of various diameters and wood types. This makes it an ideal tool for preparing winter fuel, clearing fallen timber, or managing woodlots. Users will appreciate its ability to cut through both softwoods and hardwoods with consistent performance, minimizing the effort required for strenuous cutting sessions. The chainsaw’s design focuses on delivering reliable power, which translates into faster cutting speeds and reduced operator fatigue, even during extended periods of use. Whether you are bucking large rounds into manageable pieces or splitting smaller branches for kindling, the 917.353710 30177 handles the demands of firewood preparation with ease. Its dependable operation ensures that you can consistently produce a steady supply of firewood, making it a valuable asset for anyone reliant on wood for heating or recreational fires. This capability underscores the chainsaw’s versatility and strong performance in practical, demanding applications.
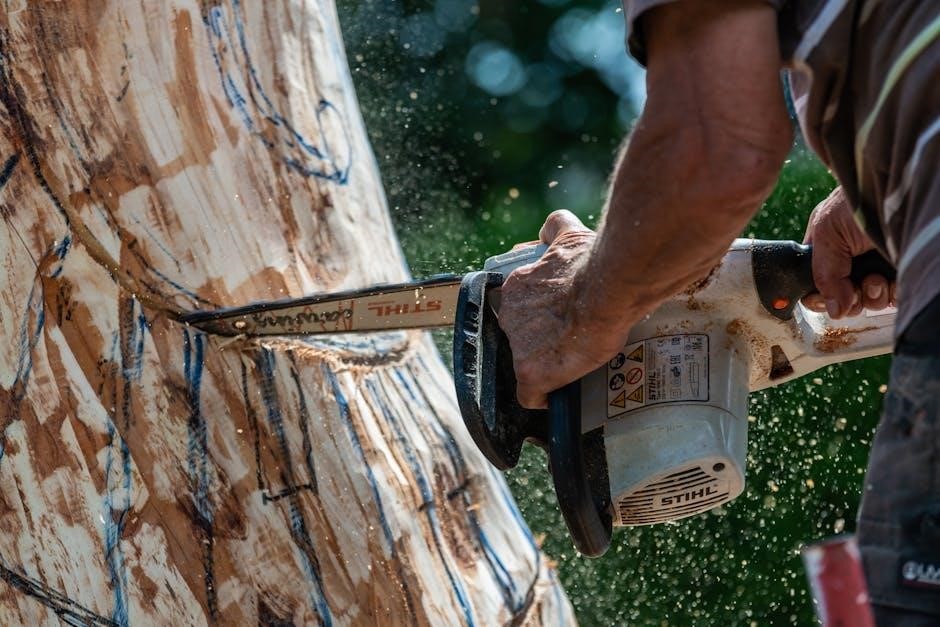

Engine Specifications and Maintenance Procedures

This section outlines vital engine specifications, including magneto and breaker-point gaps. It details maintenance procedures for ignition components, such as coil drying at 150°F for two hours, and essential ohmmeter checks.
Magneto Air Gap (0.005-0.010 inch)
The magneto air gap is a critical specification for the proper functioning of your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 ignition system. As specified in the manual, this gap should be precisely maintained between 0.005 and 0.010 inch. This small but crucial distance directly impacts the efficiency of the spark plug firing, ensuring consistent and reliable engine starts and smooth operation.
An incorrectly set magneto air gap can lead to a variety of performance issues. If the gap is too wide, the magnetic field might not induce a strong enough current in the coil, resulting in a weak spark or no spark at all. This can cause starting difficulties, misfires, or even complete engine failure. Conversely, if the gap is too narrow, there’s a risk of the magneto components making contact, leading to wear and potential damage, which also impairs spark generation.
Regular inspection and adjustment of the magneto air gap are essential components of routine engine maintenance. Using a non-magnetic feeler gauge is the recommended method for accurately measuring this distance. Always refer to your Craftsman 917.353710 30177 manual for detailed instructions on how to access the magneto and perform this adjustment correctly. Maintaining the specified gap ensures optimal ignition timing and overall engine health, extending the lifespan and performance of your chainsaw for various demanding tasks. This precise setting is fundamental for peak operational efficiency.
Breaker-Point Gap (0.015 inch)
For your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177, the manual explicitly states that the breaker-point gap should be maintained at a precise 0.015 inch. This specific measurement is crucial for the proper functioning of the engine’s ignition system, playing a direct role in the timing of the spark and the overall efficiency of combustion.
The breaker points are mechanical switches that open and close, interrupting the primary circuit of the ignition coil. This interruption causes a rapid collapse of the magnetic field in the coil, inducing a high voltage in the secondary winding, which then travels to the spark plug. An accurately set breaker-point gap ensures that this interruption occurs at the correct moment in the engine’s cycle.
If the breaker-point gap is too wide, the points may open too early or remain open for too long, leading to a weak spark or misfiring, and potentially difficult starting. Conversely, if the gap is too narrow, the points might not open sufficiently or close too quickly, causing the coil to not fully charge, resulting in a similar weak spark condition. This can also lead to premature wear of the points themselves.
Regular inspection and adjustment of this gap are vital for maintaining peak engine performance and reliability. Always use a feeler gauge to accurately measure the gap and follow the specific instructions provided in your Craftsman 917.353710 30177 manual for adjustment. Correctly setting this 0.015-inch gap is fundamental for consistent ignition and optimal chainsaw operation across all tasks.

Coil Moisture Identification
Identifying moisture within the ignition coil of your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 is crucial for troubleshooting poor performance. Moisture can significantly impede the coil’s ability to generate a strong, consistent spark, leading to various operational issues. One primary indicator is difficulty starting the chainsaw, particularly in damp or humid conditions, or after the unit has been exposed to rain or excessive condensation. The engine might crank but fail to ignite, or it may start only to run very roughly, misfire frequently, or exhibit a noticeable loss of power under load.
A common sign of internal coil moisture is an intermittent or absent spark at the spark plug, even when other ignition components like the spark plug itself and the breaker points appear to be in good working order. While visible water might not always be present on the exterior, internal dampness can create short circuits or increase resistance, preventing the coil from building sufficient voltage. If your chainsaw displays these symptoms, especially after being stored in a less-than-ideal, humid environment, or after direct exposure to moisture, suspicion of a damp coil is highly warranted. Before considering replacement, identifying and addressing this moisture is the logical next step to restore reliable ignition.
Coil Drying Method (Baking)
If your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177’s ignition coil is suspected of containing moisture, a proven method to rectify this is a controlled baking process. This gentle heating technique is designed to evaporate any trapped dampness without damaging the coil’s delicate internal windings or insulation. To perform this, first, carefully remove the ignition coil from the chainsaw. Ensure it is clean and free of external debris before proceeding. The manual specifies baking the coil in an oven. Set your oven to a precise temperature of 150 degrees Fahrenheit (150 dgf). It is crucial to maintain this low temperature to prevent overheating, which could permanently damage the coil. Once the oven reaches the target temperature, place the coil inside. Allow the coil to bake for a duration of exactly two hours. This period ensures thorough drying, allowing all internal moisture to dissipate effectively. After the two hours, turn off the oven and let the coil cool down gradually inside the oven, or on a heat-resistant surface, before handling or reinstalling it. This careful procedure can often restore a moisture-compromised coil to full functionality, saving the expense of replacement. Always handle components with care.
Coil Baking Temperature (150 dgf)
For the Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177, if moisture is suspected within the ignition coil, the manual explicitly specifies a precise baking temperature for effective drying. The recommended temperature is 150 degrees Fahrenheit (150 dgf). This specific setting is critical because it is high enough to facilitate the evaporation of water molecules trapped within the coil’s windings and insulation, yet low enough to prevent any heat-related damage to the delicate internal components. Exceeding this temperature could lead to irreversible damage, such as melting insulation, altering wire properties, or causing short circuits, rendering the coil inoperable. Conversely, a temperature significantly below 150 dgf might not be sufficient to thoroughly dry the coil within the recommended two-hour duration, leaving residual moisture that could still impair ignition performance. Therefore, when attempting to dry a coil, it is paramount to use an oven with accurate temperature control. Verifying the oven’s calibration or using an external thermometer can help ensure the 150 dgf is consistently maintained throughout the baking process; Adhering strictly to this temperature ensures the coil is safely and effectively reconditioned, restoring its proper function without risk of further damage, and is a key step in troubleshooting ignition issues.
Coil Baking Duration (Two Hours)
For the Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 manual, the recommended duration for baking a moisture-suspected ignition coil is precisely two hours. This specific timeframe is crucial for ensuring complete and effective drying of the internal components. Moisture can significantly impair the coil’s performance, leading to misfires or complete ignition failure. A duration of two hours allows sufficient time for any trapped water molecules to thoroughly evaporate from the coil’s windings and insulation, even from deep within the material. Adhering to this prescribed period is vital; a shorter baking time might not fully extract all moisture, leaving the coil susceptible to continued operational issues. Conversely, while a longer duration might seem harmless, the manual specifies two hours as the optimal balance for effective drying without unnecessary energy consumption or prolonged exposure to heat. This careful calibration ensures the coil is restored to its proper, dry condition, thereby re-establishing reliable electrical conductivity and insulation integrity necessary for consistent spark generation. Following the two-hour guideline is a critical step in the troubleshooting and maintenance process for this specific Craftsman chainsaw model, directly contributing to the restoration of its ignition system’s functionality.
Ohmmeter Checks for Ignition Components
An ohmmeter is an indispensable tool for diagnosing ignition system issues within your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177. As the manual suggests, using an ohmmeter allows for the precise evaluation of critical components such as the coil, condenser, and breaker points. For the ignition coil, you would typically check both the primary and secondary windings for proper resistance values and continuity. Deviations from the specified resistance, or an open circuit, indicate a faulty coil, potentially the Craftsman/Roper 3.7 coil mentioned. The ohmmeter can also detect short circuits within the windings. When testing the condenser, an ohmmeter helps identify if it’s shorted or open, which would prevent it from effectively storing and discharging electrical energy, impacting spark quality. Similarly, the breaker points require verification with an ohmmeter to ensure they open and close properly, providing continuity when closed and an open circuit when open, facilitating the interruption of the primary circuit. Comparing these measured readings against the service manual’s specifications is crucial for accurately pinpointing defective parts and ensuring the ignition system functions optimally.
Craftsman/Roper 3.7 Coil Specifics
The Craftsman/Roper 3.7 coil is a critical component within the ignition system of your 917.353710 30177 chainsaw, responsible for transforming low-voltage current into the high-voltage spark necessary for engine combustion. Understanding its specific characteristics is vital for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. If you suspect moisture infiltration, the manual suggests a coil drying method: baking it in an oven at 150 dgf for two hours; This procedure is specifically designed to remove any internal dampness that could impede its electrical performance. Furthermore, assessing the integrity of this particular coil often involves using an ohmmeter. This tool allows you to check the resistance of both the primary and secondary windings, ensuring they fall within the manufacturer’s specified range for the Craftsman/Roper 3.7. Discrepancies, such as an open circuit or a short, indicate a faulty coil that needs replacement. Precise resistance values for this specific model are crucial for accurate diagnosis, highlighting the importance of consulting the detailed service manual. Verifying the coil’s functionality is paramount for maintaining reliable engine operation and consistent starting performance.

Safety and Product Support Resources
Adhering to safety rules and operating instructions is paramount for your chainsaw’s safe use. CRAFTSMAN offers comprehensive parts, service, and warranty information to support your product throughout its lifespan, ensuring reliability and performance.
Adherence to Safety Rules
The Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 manual explicitly emphasizes the critical importance of adhering strictly to all outlined safety rules. Before commencing any operation, it is absolutely paramount to thoroughly read and comprehend every safety instruction provided. This dedication to understanding minimizes risks associated with powerful machinery like this robust gas-powered engine. Failure to meticulously follow these guidelines can lead to severe personal injury, significant property damage, or even fatal accidents. The comprehensive manual, often including a dedicated safety section, serves as your primary guide for responsible usage. It meticulously details proper handling techniques, essential personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, and crucial environmental considerations to establish a safe working environment. Understanding kickback prevention strategies, correct body positioning, and safe starting procedures are fundamental for every user. This product, featuring a low emission engine, operates differently from older models, necessitating careful attention to its specific operational nuances detailed within the safety section. Regular review of these rules, alongside proper maintenance, ensures consistent safety. Always prioritize safety for yourself and others when operating the Craftsman 917.353710 30177 chainsaw, ensuring a secure and productive cutting experience.
Following Operating Instructions
Following the operating instructions for your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 is absolutely paramount for safe and effective use. The manual serves as the definitive guide, detailing every step from initial setup to proper shutdown procedures. It is critically important to read and understand all instructions thoroughly before attempting to operate the chainsaw. This specific model features a low emission engine, which operates differently from older designs, meaning its unique operational characteristics are meticulously explained within the manual. Adhering to these specialized instructions ensures the engine functions optimally and efficiently, preventing potential damage and prolonging its lifespan.
For versatile tasks such as landscaping and firewood cutting, the manual outlines the correct techniques and approaches, allowing you to maximize the capabilities of its robust gas-powered engine. Ignoring these detailed guidelines can lead to improper operation, reduced performance, and increased risk of accidents. The instructions cover essential aspects like fuel mixing, starting procedures, cutting methods, and proper handling for various applications. By diligently following each step, users can maintain peak performance, enhance safety, and ensure the longevity of their Craftsman chainsaw, making every project more manageable and secure. Consistent adherence to these instructions is not merely a suggestion but a fundamental requirement for responsible chainsaw ownership and operation.
CRAFTSMAN Parts and Service

When your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 requires attention for maintenance or repairs, accessing reliable CRAFTSMAN Parts and Service is crucial. Products naturally experience wear over time, necessitating either genuine replacement components or professional repair work. Fortunately, Craftsman provides robust support options to ensure your chainsaw remains in optimal working condition, delivering dependable performance for all your landscaping and cutting needs.
Should you need to fix your product, Craftsman offers convenient avenues for assistance. This includes securing authentic CRAFTSMAN replacement parts, essential for maintaining the original performance, safety, and integrity of your chainsaw. For the 917.353710 30177, official channels help locate and acquire specific components efficiently. If issues extend beyond simple part replacement, Craftsman’s extensive service network provides expert assistance. They can guide users through troubleshooting or direct them to authorized service centers for complex diagnostic and repair services. Comprehensive information on warranty, available parts, and service procedures is typically found on the official Craftsman website or by directly contacting their customer support. This integrated system ensures owners have the necessary resources to keep their robust gas-powered chainsaw performing powerfully and safely throughout its lifespan.
CRAFTSMAN Warranty Information
Understanding the warranty for your Craftsman Chainsaw 917.353710 30177 is a vital aspect of product ownership, ensuring peace of mind regarding potential manufacturing defects. Craftsman typically provides comprehensive warranty coverage for its tools, protecting against issues arising from material or workmanship flaws under normal use conditions. It’s crucial for owners to consult the specific warranty details included with their manual or available on the official Craftsman website. This information outlines the duration of coverage, what types of repairs or replacements are included, and the procedures for making a warranty claim. Adhering to the operating instructions and recommended maintenance procedures, as detailed in the chainsaw’s manual, is often a prerequisite for maintaining warranty validity. For instance, proper engine care ensures the low emission engine operates as intended. The warranty provides a layer of product support, allowing customers to address unforeseen issues without incurring additional costs, thereby extending the useful life and reliability of their robust gas-powered chainsaw. Owners should familiarize themselves with these terms to fully leverage available support, ensuring their Craftsman tool continues to perform effectively for various tasks, including landscaping and firewood cutting.